
For instance, creating marketing materials in-house may save money short-term but cost more in productivity compared to outsourcing. Fixed overhead items like rent, insurance, and long-term contracts are often assumed to be unchangeable. However, proactive renegotiation can yield cost savings, especially in times of overhead cost examples economic change or business restructuring. Some businesses operate in high-cost environments or offer premium services that justify higher overhead.
- In this case, you may want to calculate your construction overhead by sales.
- We research and recommend products and services suitable for various business types, investing thousands of hours each year in this process.
- Variable overhead costs vary in proportion to the volume of output generated.
- It comprises all indirect costs, whether in the form of Indirect material, indirect Labor, or Indirect Expenses, which are incurred in the manufacturing of the goods and services.
- With business.com+, members get dedicated support, exclusive deals and expert advice.
- By calculating the proportion of each type of overhead, companies can determine their break-even points and set prices that ensure profitability.
- Manufacturing overhead is the sum of all the manufacturing costs except direct labor or direct materials costs.
Calculate your overhead rate
Efficiency variance measures the difference between actual and budgeted hours multiplied by the standard rate, reflecting how efficiently resources are used. Spending variance compares actual costs to the budgeted rate, highlighting Cash Disbursement Journal cost control issues. You provide a phenomenal product or service, work with your clients to ensure they’re satisfied, and get paid when all i… Your Project B estimate is $1,000, with $900 in costs ($600 labor, $240 materials, and $60 overhead).
What does a favorable Variable Overhead Spending Variance indicate?
Examples of semi-variable overheads include sales commissions, vehicle usage, and some utilities such as power and water costs that have a fixed charge plus an additional cost based on the usage. For businesses that still require a physical presence, hybrid work policies can help balance team collaboration with reduced space and overhead costs. Hot-desking systems or shared coworking spaces are effective solutions for managing office occupancy efficiently. In restaurants, hotels, and other hospitality services, overhead plays a massive role in determining profitability. The combination of real estate, staffing, utilities, and regulatory compliance often results in high fixed and semi-variable costs.
- Manufacturing businesses often deal with extensive overhead costs that support the production process but are not directly tied to the materials or labor used in creating goods.
- This Manufacturing Overhead Cost Per Unit needs to be added to the direct material and direct labor costs to determine the full Cost of Goods Manufactured for each unit.
- Fixed overhead costs are overhead expenses that remain constant regardless of your business activity.
- Still, your accountant will need to allocate these costs to the goods manufactured.
Types of overhead costs
Reducing overhead isn’t only about trimming expenses; it’s also about redirecting resources into value-generating activities. Businesses that reallocate saved overhead toward marketing, innovation, employee development, or client acquisition often see a stronger return. With better visibility into recurring and fluctuating costs, businesses can plan more effectively and respond quickly to unexpected changes. Automation also helps in identifying trends that would be difficult to spot manually.
Underinsuring can expose a business to financial risk, while overinsuring wastes valuable resources. Too much overhead can eat into profit margins and leave little room for reinvestment or growth. Conversely, strategically reducing unnecessary overhead can improve profitability and operational efficiency. By tracking and categorizing overhead, businesses gain clarity on their financial standing and are better prepared to make informed decisions.

Monitoring overhead costs helps identify unnecessary or excessive expenses that can be reduced without compromising operational quality. For instance, automating routine tasks with tools like Deskera ERP can streamline processes, cut administrative costs, and improve overall efficiency. Add up all the overhead expenses to get the https://cellixhome.eraenterprise.id/fob-shipping-point-vs-fob-destination-explained/ total overhead cost for a specific period, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually.
A. Fixed Overheads
In such cases, the overhead costs indirectly incurred to support that product represent expenses that are better eliminated to protect overall profitability. The high variability of overhead expenses—particularly in larger organizations—makes managing and predicting overhead costs challenging. This variability has significant implications for pricing decisions, as products with fluctuating cost structures may be underpriced, leading to financial losses. The designation “indirect” refers to all costs and expenses incurred by a company, separate from production-related costs, which constitute overhead costs.
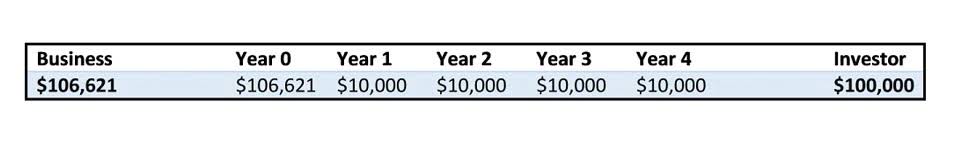
Why is Variable Overhead important for cost control?
A software development company offers yoga and meditation classes to its employees during work hours. The company classifies these classes as a fringe benefit, considering them part of the overall wellness program aimed at improving employee well-being. The company carefully documents the classes and consults with a tax advisor to understand the tax implications of the program.
